- Permissions Reset App
- Permissions Reset Big Sur
- Permissions Reset Mac Catalina
- Reset Windows 10 Default Permissions
- Permissions Reset Mac App Catalina
File permissions control who can and cannot open a file on the system or network or directory they reside on. Change file permissions on Windows 10. To change file permissions on Windows 10, follow these steps after signing in with the correct user account needed for the job. Open File Explorer. Navigate to the file you want to change. Authorization will only be granted if the user is authenticated and has the relevant per-object permissions and relevant model permissions assigned. POST requests require the user to have the add permission on the model instance. PUT and PATCH requests require the user to have the change permission on the model instance. Resets all permissions any principals have on a SCO to the permissions of its parent SCO. If the parent has no permissions set, the child SCO will also have no permissions. You can allow or block permissions for a specific site. The site will use its settings instead of the default settings. You can also clear data for a site. On your computer, open Chrome. Go to a website. To the left of the web address, click the icon you see: Lock, Info, or Dangerous. Click Site settings. Change a permission setting.
-->APPLIES TO: 2013 2016 2019 SharePoint in Microsoft 365
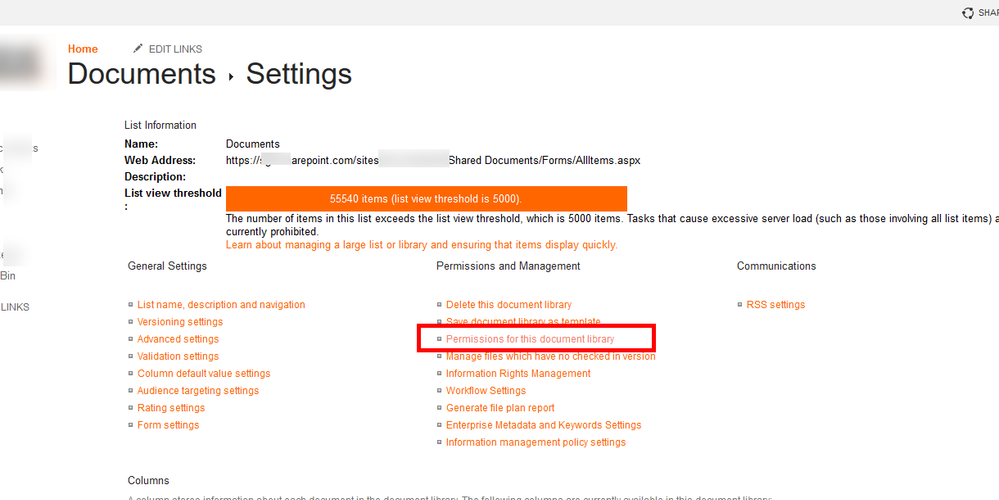
Default permission levels are predefined sets of permissions that you can assign to individual users, groups of users, or security groups, based on the functional requirements of the users and on security considerations. SharePoint Server permission levels are defined at the site collection level and are inherited from the parent object by default.
Default permission levels
Default permission levels are made up of a set of permissions that enable users to perform a collection of related tasks. SharePoint Server includes seven permission levels. You can customize the permissions contained within five of these permission levels. You cannot customize the permissions within the Limited Access and Full Control permission levels.
Note
Although you cannot directly edit the Limited Access and Full Control permission levels, you can make individual permissions unavailable for the entire web application, which removes those permissions from the Limited Access and Full Control permission levels. For more information, see Manage permissions for a web application in SharePoint Server.
The following table lists the default permission levels for team sites in SharePoint Server.
| Permission level | Description | Permissions included by default |
|---|---|---|
| View Only | Enables users to view application pages. The View Only permission level is used for the Excel Services Viewers group. | View Application Pages View Items View Versions Create Alerts Use Self Service Site Creation View Pages Browse User Information Use Remote Interfaces Use Client Integration Features Open |
| Limited Access | Enables users to access shared resources and a specific asset. Limited Access is designed to be combined with fine-grained permissions to enable users to access a specific list, document library, folder, list item, or document, without enabling them to access the whole site. Limited Access cannot be edited or deleted. | View Application Pages Browse User Information Use Remote Interfaces Use Client Integration Features Open |
| Read | Enables users to view pages and list items, and to download documents. | Limited Access permissions, plus: View Items Open Items View Versions Create Alerts Use Self-Service Site Creation View Pages |
| Contribute | Enables users to manage personal views, edit items and user information, delete versions in existing lists and document libraries, and add, remove, and update personal Web Parts. | Read permissions, plus: Add Items Edit Items Delete Items Delete Versions Browse Directories Edit Personal User Information Manage Personal Views Add/Remove Personal Web Parts Update Personal Web Parts |
| Edit | Enables users to manage lists. | Contribute permissions, plus: Manage Lists |
| Design | Enables users to view, add, update, delete, approve, and customize items or pages in the website. | Edit permissions, plus: Add and Customize Pages Apply Themes and Borders Apply Style Sheets Override List Behaviors Approve Items |
| Full Control | Enables users to have full control of the website. | All permissions |
If you use a site template other than the team site template, you will see a different list of default SharePoint permission levels. For example, the following table shows additional permission levels provided with the publishing template.
| Permission level | Description | Permissions included by default |
|---|---|---|
| Restricted Read | View pages and documents. For publishing sites only. | View Items Open Items View Pages Open |
| Approve | Edit and approve pages, list items, and documents. For publishing sites only. | Contribute permissions, plus: Override List Behaviors Approve Items |
| Manage Hierarchy | Create sites; edit pages, list items, and documents, and change site permissions. For Publishing sites only. | Design permissions minus the Approve Items, Apply Themes and Borders, and Apply Style Sheets permissions, plus: Manage permissions View Web Analytics Data Create Subsites Manage Alerts Enumerate Permissions Manage Web Site |
User permissions
SharePoint Server includes 33 permissions, which are used in the default permission levels. You can configure which permissions are included in a particular permission level (except for the Limited Access and Full Control permission levels), or you can create a new permission level to contain specific permissions.
Permissions are categorized as list permissions, site permissions, and personal permissions, depending on the objects to which they can be applied. For example, site permissions apply to a particular site, list permissions apply only to lists and libraries, and personal permissions apply only to certain objects, such as personal views and private Web Parts. The following tables describe what each permission is used for, the dependent permissions, and the permission levels in which it is included.
List permissions
| Permission | Description | Dependent permissions | Included in these permission levels by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manage Lists | Create and delete lists, add or remove columns in a list, and add or remove public views of a list. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Edit, Design, Full Control, Manage Hierarchy |
| Override List Behaviors | Discard or check in a document that is checked out to another user, and change or override settings that allow users to read/edit only their own items. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Design, Full Control |
| Add Items | Add items to lists, and add documents to document libraries. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Edit Items | Edit items in lists, edit documents in document libraries, and customize Web Part pages in document libraries. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Delete Items | Delete items from a list, and documents from a document library. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| View Items | View items in lists, and documents in document libraries. | View Pages, Open | Read, Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Approve Items | Approve a minor version of list items or document. | Edit Items, View Items, View Pages, Open | Design, Full Control |
| Open Items | View the source of documents with server-side file handlers. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Read, Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| View Versions | View past versions of a list item or document. | View Items, Open Items, View Pages, Open | Read, Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Delete Versions | Delete past versions of list items or documents. | View Items, View Versions, View Pages, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Create Alerts | Create alerts. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Read, Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| View Application Pages | View forms, views, and application pages. Enumerate lists. | Open | All |
Site permissions
| Permission | Description | Dependent permissions | Included in these permission levels by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manage Permissions | Create and change permission levels on the web site and assign permissions to users and groups. | View Items, Open Items, View Versions, Browse Directories, View Pages, Enumerate Permissions, Browse User Information, Open | Full Control |
| View Web Analytics Data | View reports on Web site usage. | View Pages, Open | Full Control |
| Create Subsites | Create subsites such as team sites, Meeting Workspace sites, and Document Workspace sites. | View Pages, Browse User Information, Open | Full Control |
| Manage Web Site | Grants the ability to perform all administration tasks for the web site, as well as manage content. | View Items, Add and Customize Pages, Browse Directories, View Pages, Enumerate Permissions, Browse User Information, Open | Full Control |
| Add and Customize Pages | Add, change, or delete HTML pages or Web Part pages, and edit the website. | View Items, Browse Directories, View Pages, Open | Design, Full Control |
| Apply Themes and Borders | Apply a theme or borders to the whole website. | View Pages, Open | Design, Full Control |
| Apply Style Sheets | Apply a style sheet (.css file) to the website. | View Pages, Open | Design, Full Control |
| Create Groups | Create a group of users that can be used anywhere within the site collection. | View Pages, Browse User Information, Open | Full Control |
| Browse Directories | Enumerate files and folders in a website by using SharePoint Designer 2013 and Web DAV interfaces. | View Pages, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Use Self-Service Site Creation | Create a website using Self-Service Site Creation. | View Pages, Browse User Information, Open | Read, Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| View Pages | View pages in a website. | Open | Read, Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Enumerate Permissions | Enumerate permissions on the website, list, folder, document, or list item. | Browse Directories, View Pages, Browse User Information, Open | Full Control |
| Browse User Information | View information about users of the website. | Open | All |
| Manage Alerts | Manage alerts for all users of the website. | View Items, View Pages, Open, Create Alerts | Full Control |
| Use Remote Interfaces | Use SOAP, Web DAV, the Client Object Model, or SharePoint Designer 2013 interfaces to access the website. | Open | All |
| Use Client Integration Features | Use features that launch client applications. Without this permission, users must work on documents locally and then upload their changes. | Use Remote Interfaces, Open, View Items | All |
| Open | Enables users to open a website, list, or folder to access items inside that container. | None | All |
| Edit Personal User Information | Enables users to change their own user information, such as adding a picture. | Browse User Information, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
Personal permissions
| Permission | Description | Dependent permissions | Included in these permission levels by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manage Personal Views | Create, change, and delete personal views of lists. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Add/Remove Personal Web Parts | Add or remove personal Web Parts on a Web Part page. | View Items, View Pages, Open, Update Personal Web Parts | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
| Update Personal Web Parts | Update Web Parts to display personalized information. | View Items, View Pages, Open | Contribute, Edit, Design, Full Control |
See also
Other Resources
If by accident you execute a command that changes the permission or ownership of a bunch of folders or file in Debian, you are in a lot of trouble, usually the sollution is to reinstall the system, but as I was unwilling to reinstall thet system, I decided to find another way to do it, as I have finally set up my system as I want it to run, so we will look into a couple of methods of how to do it without reinstallation of the system.
Using virtual machine, reinstalling packages, or even generating a script from debian packages.
I accidently ran a chown command on the whole /var folder, and ended up with every file and folder in ownership of www-data.
According to the manual the var directory is:
The /var directory is mostly mounted as a separate filesystem under the root where in all the variable content like logs, spool files for printers, crontab,at jobs, mail, running process, lock files etc. Care has to be taken in planning this file system and maintenance as this can fill up pretty quickly and when the FileSystem is full can cause system and application operational issues.
I wanted to chown all the hidden files in the directory /var/www to www-data, I was in the directory /var/www when I ran the following command
And after running this, I noticed that my whole var folder was in ownership of www-data, so my quest to restore it to the original ownership and permissions started.
Imagine if it was rm instead of chown, I would have ended up deleting all the files in the var folder.
If you ever what to do something with the hidden files you should use the following approach, what I should have written should have been:
This command properly sets the hidden folders to the correct owners
Permissions Reset App
So now I ended up with a var folder with a lot of messed up ownerships, so how to restore them.
There are multiple ways to do it, although the only way to completly restore them as they were would require you to deploy on a virtual machine, and copy the properties, that is the surest way so they are restored correctly
Method 1: Virtual Machine
Start installing you distribution on the virtual machine, and while you are waiting for the instalation to finish you need to prepeare some data needed for restoration of your machine.
This doesn’t have to happen on your machine, you can easily create a virtual machine on any computer and use the data to restore your own.
All the commands here are run as root.
We need a list of all your installed packages so they can be restored on the virtual machine, to get them, execute the following command
By now the machine should have finished installing, so let’s prepare some of the necessities, I use a pinning and a lot of repositores, including testing, unstable, stable, plus 3rd party repositories, so to do so we need to transfer the contents of /etc/apt to the virtual machine, you should know how to transfer the files to the virtual machine.
We also need to transfer the keys, because you can’t copy the keys we need to export them.
And then transfer them to the virtual machine, and run the import for keys
If you are using multiarch you will have to add the appropriate architecture into the system, in my case I’m using also i386 libraries for skype, so I executed this on my virtual machine
Now we need to install all the packages that are on our system, so let’s run the following commands on the virtual machine
Now you can leave your virtual machine for a while, while it downloads all the packages and installs them.
After the installation has finished you can reboot your system, and after it boots, we need to extract all the information so we can restore it successfully.
On the virtual machine run the following command:
Now you transfer the generated file /tmp/var.permissions.txt to your machine, and you run the following script to restore everything as it was
This is one way to restore them and it’s probably the best way to restore them
Permissions Reset Big Sur
FreeBSD
If you have FreeBSD you can use mtree to copy over the permissions and restore them, the first line creates a list of the permissions and owners the second one restores them
Method 2: From the debian packages
You can also restore permissions from the debian packages, but not the owners, as it doesn’t contain that information, it will restore them to how they are suppose to be when installing them the first time, but the permissions will be restored correctly.’
There are two ways to do this, you can restore them from the debian cache which is located in /var/cache/apt/archives/, but if you ever issued apt-get clean you will not have all the packages there, or you can just download all the packages and restore them like that, the script will be the same for both approaches.
So let’s create a new folder in opt, called restore
I called my script create_permissions_script.sh, and I put it in /opt/restore, it is designed to work from the local directory the script is in.


This script reads all the packages, extracts the file list including permissions and owners, parses it and then stores it in a file so you can restore it.
This script will generate a new script called restore_permissions.sh, which contains all the neccesseary commands like chown and chmod for all the directories and files, executing this script will correct all the ownerships and permissions as they need to be after installation of the package in question
So let’s download the packages, or if you choose to restore them from the cache folder you can skip this step, just copy over this script to the cache folder and you are done, if you are like me and you ocasionally clean up the folder, you will have to download all the packages first
Executing that line will download all the packages into the directory, as this will take a while, you can take a break.
After all the packages finish downloading, you need to run the script for generating the permissions and owners, this will also take a while to read and process all debian packages
After this is finished you will see that you have a script called restore_permissions.sh, and running it will restore the permissions
Permissions Reset Mac Catalina
Reset Windows 10 Default Permissions
Method 3: Reinstalling with aptitude
Permissions Reset Mac App Catalina
You can reinstall all the packages using aptitude, but this is a really slow process, but if you want to you can do like so
